Unggulan
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Ideal Gas Law R Values : Phy351 ch 1 ideal law, gas law, condensed, triple point ... - Here comes the tricky part when it comes to the gas constant , r.
Ideal Gas Law R Values : Phy351 ch 1 ideal law, gas law, condensed, triple point ... - Here comes the tricky part when it comes to the gas constant , r.. Substitute these values into equation. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for pressure given moles, universal gas constant, temperature and volume. The ideal gas law can be written in terms of avogadro's number as pv = nkt, where k, called the boltzmann's constant, has the value k = 1.38 × 10 −23 j/k. Ideal gas law is used in stoichiometry in finding the number of moles/volume a given gas can produce when temperature and pressure are kept constant. The gas constant (also known as the molar gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol r or r.
The kinetic theory of gases. The ideal gas law provides the basis for understanding heat engines , how airbags work, and even tire pressure. There is no such thing as an ideal gas, of course, but many gases behave approximately as if they were ideal at ordinary working temperatures and pressures. Lower pressure is best because then the average. The units of the universal gas constant r is derived from equation pv = nrt.

To account for deviation from the ideal situation an other factor.
Here comes the tricky part when it comes to the gas constant , r. While this law specifically applies to ideal gases, most gases approximate the ideal gas law under most conditions. The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with newton's laws. The classical carnot heat engine. The ideal gas law can be written in terms of avogadro's number as pv = nkt, where k, called the boltzmann's constant, has the value k = 1.38 × 10 −23 j/k. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes. The constant r is called the ideal gas law constant. Value of r will change when dealing with different unit of pressure and volume (temperature factor is overlooked because. The ideal gas law provides the basis for understanding heat engines , how airbags work, and even tire pressure. The ideal gas law does not work well at very low calculate the molar mass of butane and convert all quantities to appropriate units for the value of the gas constant. The kinetic theory of gases. The units of the universal gas constant r is derived from equation pv = nrt.
The ideal gas law was first written in 1834 by emil clapeyron. Say out loud liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. this is not the only value of r that can exist. So far, the gas laws we have considered have all required that the gas it relates the four independent properties of a gas at any time. This ideal gas law calculator is also known as a gas pressure calculator, a molar volume calculator or a gas volume calculator because you can use it to find different values. Here are the steps to follow when using this online tool
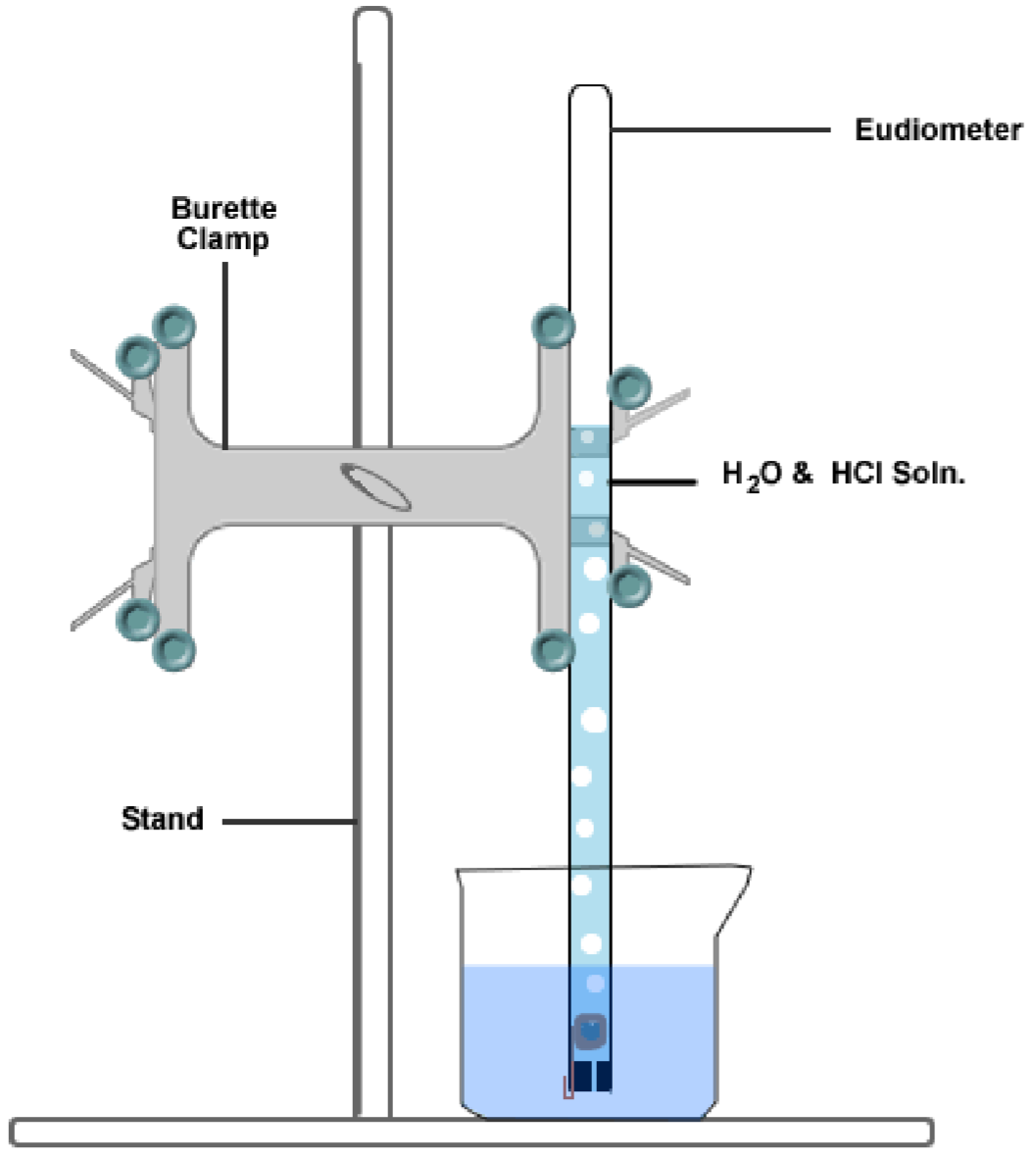
This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes.
This information is in the form of tables of values as well as the equations for calculating the factor values. Molar, universal, ideal gas constant, si unit, english units, formula, values, specific gas constant, 8.314 j/mol/k, 0.082 latm/mol/k 7 boltzmann's constant and ideal gas constant. The value of r depends on the units involved, but is usually an ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles whose only interactions are perfectly elastic collisions. The value and units of r depend on the units used in determining p, v. The units of the universal gas constant r is derived from equation pv = nrt. The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for pressure given moles, universal gas constant, temperature and volume. This ideal gas law calculator is also known as a gas pressure calculator, a molar volume calculator or a gas volume calculator because you can use it to find different values. Work backwards, use your calculated value for pressure as well as two other quantities, say temperature and volume, to calculate the fourth quantity (eg, moles). Here are the steps to follow when using this online tool A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; Say out loud liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. this is not the only value of r that can exist.
The value of r depends on the units used. A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. The value for r will depend on what units you are using for the properties of the gas. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes.
The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin.
It is a good approximation to the behavior the state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. Here are the steps to follow when using this online tool As the numerical values of. If the pressure p is in atmospheres (atm), the volume v is in liters (l), the moles n is in moles (mol), and temperature t is in kelvin (k), then r lastly, this video may help introduce you to the ideal gas law. The ideal gas law does not work well at very low calculate the molar mass of butane and convert all quantities to appropriate units for the value of the gas constant. The ideal gas law was first written in 1834 by emil clapeyron. 8 gas constant in other important equations. A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; The ideal gas law is: The ideal gas law states that p x v = n x r x t where, p is pressure, v is volume, n is number of moles of the gas, r is the ideal gas constant and t is temperature in kelvin. The approximate value is generally accurate under many conditions. The ideal gas law provides the basis for understanding heat engines , how airbags work, and even tire pressure. Its value depends on the units used.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Postingan Populer
Wolf Anime Boy Sad : Pin on My board when I'm sad I add to the board / Anime gifs manga anime anime art anime wolf female anime anime demon hot anime otaku anime boy, crying, sad, blue hair, blue eyes, water;
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Balearic Islands Menorca : Arenal D En Castell Menorca Balearic Islands Spain ... / Balearic island beaches from menorca to ibiza.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Komentar
Posting Komentar